Ingress Access Rules
Using Ingress rules, you can specify that external visitors can access services through specific paths.
1.1 Feature Introduction
Ingress rules expose services within a Kubernetes cluster over HTTP or HTTPS protocols. It is suitable for web-based applications such as TensorBoard, Visdom, Jupyter, etc. By using Ingress rules, you can specify that external visitors can access services through specific paths.
For example, if you want to access services through TensorBoard or Visdom, expose the service to the corresponding port within the container, and map them to the service in the cluster. The Ingress controller will automatically handle these requests, forward them to the corresponding service in the cluster, and support HTTPS and HTTP protocols as needed.
Advantages:
- Suitable for exposing web services.
- Supports HTTP/HTTPS protocols.
Use Cases:
- Access TensorBoard.
- Access Visdom.
- Access Jupyter Notebook.
Forwarding Path: All access paths use a unified format: crater.act.buaa.edu.cn/ingress/{userName}-{uuid}. Here, userName is the username, and uuid is a five-character identifier automatically generated, pointing to a specific service.
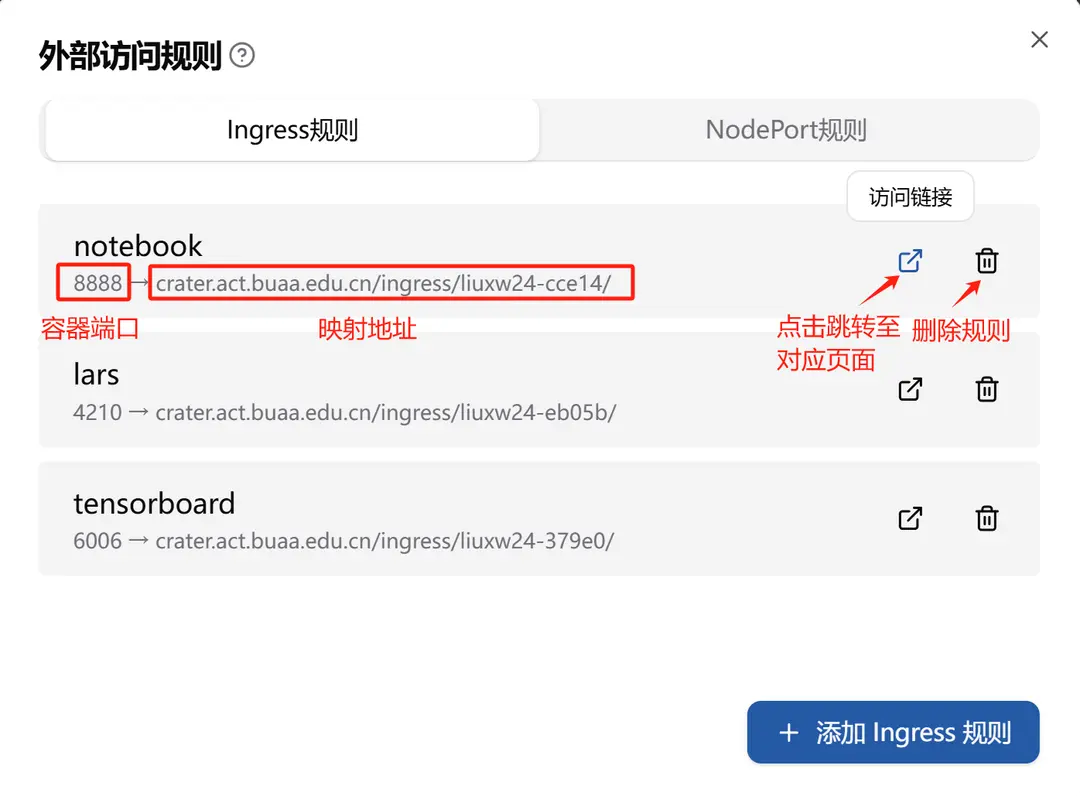
After the configuration is completed, you can see the following content in the corresponding Pod's Annotations, using ingress.crater.raids.io as the key:
metadata:
annotations:
crater.raids.io/task-name: tensorboard-example
ingress.crater.raids.io/lars: '{"Name":"lars","Port":4210,"Prefix":"/ingress/liuxw24-eb05b/"}'
ingress.crater.raids.io/tensorboard: '{"Name":"tensorboard","Port":6006,"Prefix":"/ingress/liuxw24-379e0/"}'
ingress.crater.raids.io/notebook: '{"Name":"notebook","Port":8888,"Prefix":"/ingress/liuxw24-cce14/"}'1.2 Usage Example
When you want to expose a web application for external access, you can use Ingress rules. For example, you can configure an Ingress rule for TensorBoard so that external users can access the service through a browser.
Setting Up an Ingress External Access Rule
The steps to set up an Ingress external access rule are as follows:
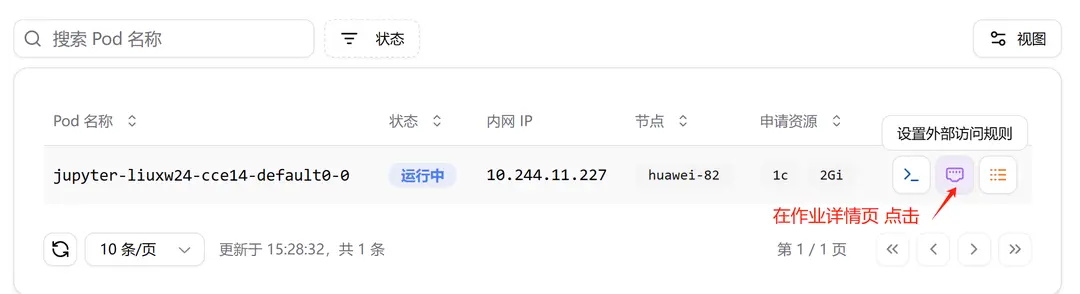
-
Click "Set External Access Rule" on the job details page.
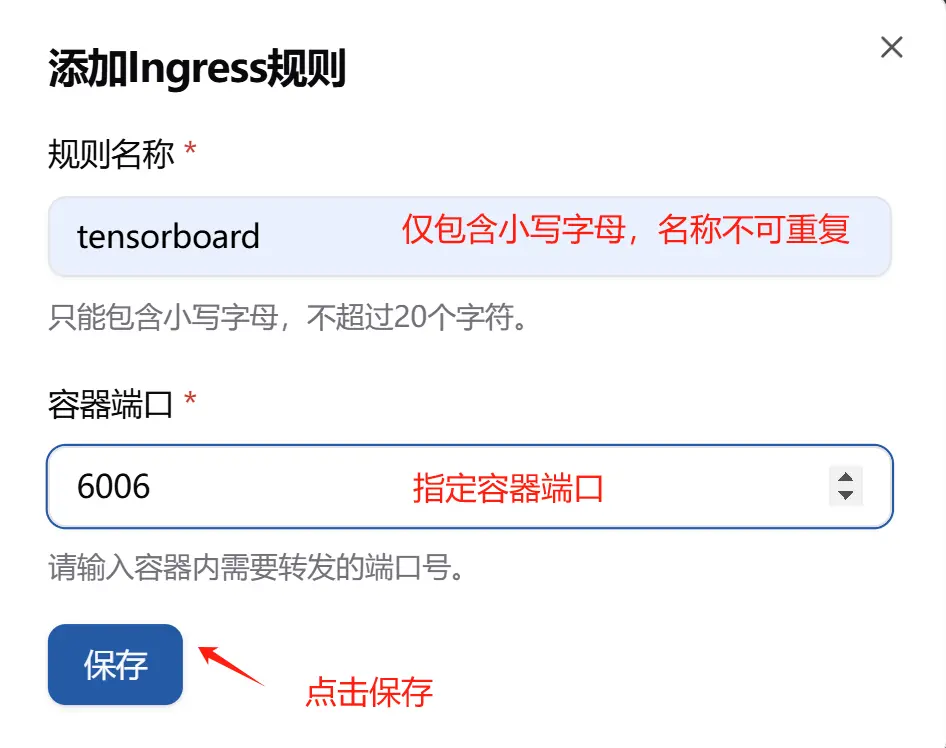
-
In the popped-up dialog box, click "Add Ingress Rule", enter the corresponding rule name (only lowercase letters, no more than 20 characters, and not duplicated), as well as the container port, and click Save.
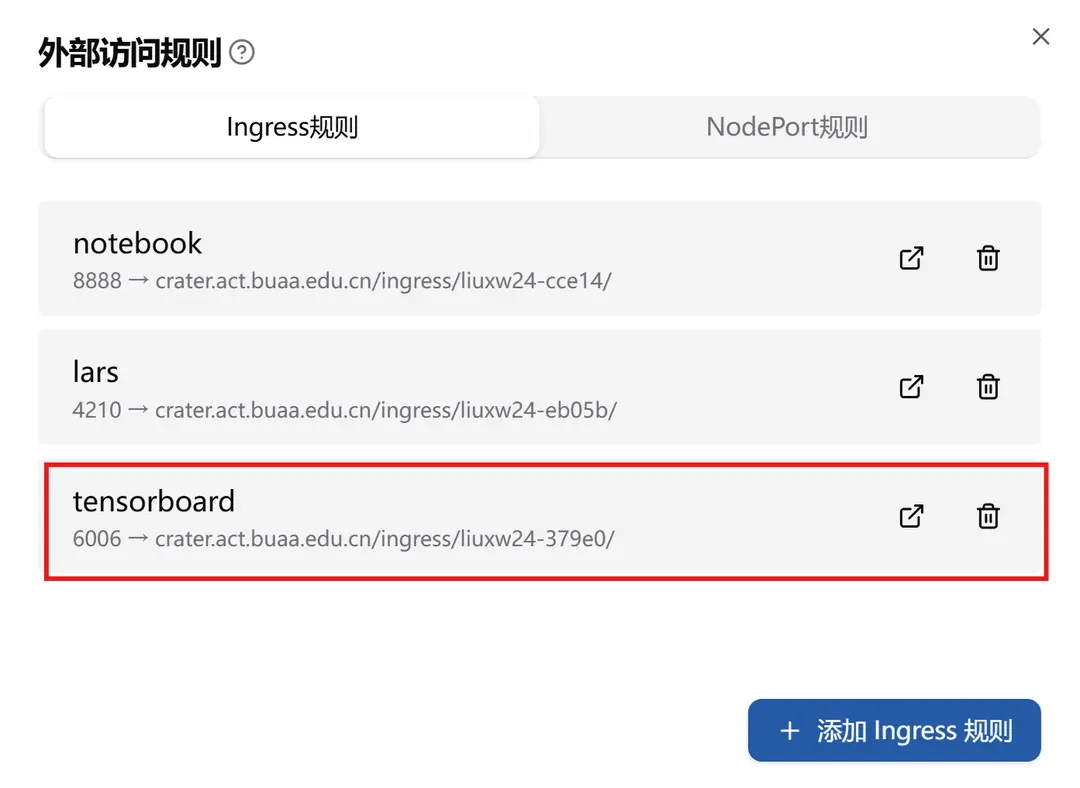
-
After saving successfully, you can see the corresponding Ingress rule.
Example Configuration:
{
"Name": "tensorboard",
"Port": 6006,
"Prefix": "/ingress/liuxw24-379e0/"
}Field Description:
- Port Number (
port): A custom port number, set to6006here because TensorBoard typically uses this port by default. - Access Path (
prefix): The access path will be mapped tocrater.act.buaa.edu.cn/ingress/{userName}-{uuid}, whereuserNameis the username anduuidis an automatically generated five-character identifier.
Starting TensorBoard Inside the Container
TensorBoard is a tool for visualizing data related to the training process of deep learning models. Usually, it starts the service at a local default URL (e.g.,
http://localhost:6006/) to display the data. However, in some scenarios, such as in a server environment or when accessing through a reverse proxy, you need to specify a custombaseurlto correctly access TensorBoard.
The method to specify baseurl is as follows (using the command line to start as an example):
When starting TensorBoard via the command line, you can use the --logdir parameter to specify the log directory, and use the --bind_all and --path_prefix parameters to set the baseurl-related options.
Assuming your TensorBoard log directory is /path/to/logs, and you want to set the baseurl to /tensorboard, you can use the following command:
tensorboard --logdir=/path/to/logs --bind_all --path_prefix=/tensorboardHere, the --bind_all parameter makes TensorBoard bind to all network interfaces, allowing it to be accessed from other machines (if this feature is needed).
The --path_prefix parameter is used to specify the baseurl part. In this example, you can access TensorBoard by visiting a URL like http://your_server_ip:6006/tensorboard (assuming the default port is 6006).
You need to start TensorBoard inside the container and perform the relevant configuration, following these steps:
Open the terminal or command prompt and run:
tensorboard --port {port} --logdir {your-logs-dir} --bind_all --path_prefix={your-ingress-prefix}The explanations for the parameters are as follows:
port: The port to be specified, defaulting to 6006{your-logs-dir}: The user-specified output directory for training data (e.g.,./logs)--bind_all: Makes TensorBoard bind to all network interfaces, allowing it to be accessed from other machines{your-ingress-prefix}: The specified Ingress access path, which is/ingress/liuxw24-379e0in this example (see the configuration under Ingress Access Rules)
Access Method:
-
Users can access TensorBoard via the path
gpu.act.buaa.edu.cn/ingress/{userName}-{uuid}and see the corresponding page as follows:
Quick Deployment of DeepSeek R1 Single-Machine Inference
This platform provides a job template for quickly deploying DeepSeek R1 single-machine inference. You can directly use it to create single-machine tasks and quickly deploy your own DeepSeek, or start the Web UI interface to interact with large models.
NodePort Access Rules
NodePort rules can expose service ports and allow external users to access them via the IP address of a cluster node and a specified port number.