Guide to Migrating Environment from Slurm Cluster
Reusing existing Conda environments or rebuilding Python environments
Overview
During the upgrade or migration of a computing cluster, environment migration is a critical step. This article will guide you on how to migrate an existing Slurm cluster environment to a new computing platform. We will focus on two main approaches: directly reusing an existing Conda environment and rebuilding a Python environment based on an existing one.
1. Reusing an Existing Conda Environment
Warning
Although you can directly reuse an existing Conda environment, we recommend carefully considering the following factors:
- Performance impact: Reinstalling a Python environment inside a Docker container typically offers better execution efficiency
- Compatibility issues: Reusing the environment directly may lead to path dependency problems
- Environment cleanliness: The existing environment may contain unused dependency packages
-
Path adjustment: Modify the mounting path, replacing
/home/{username}with/home/LAB/{username}to align with the Slurm cluster and resolve hard-coded path issues. If you do not need to reuse the environment, you can skip this step.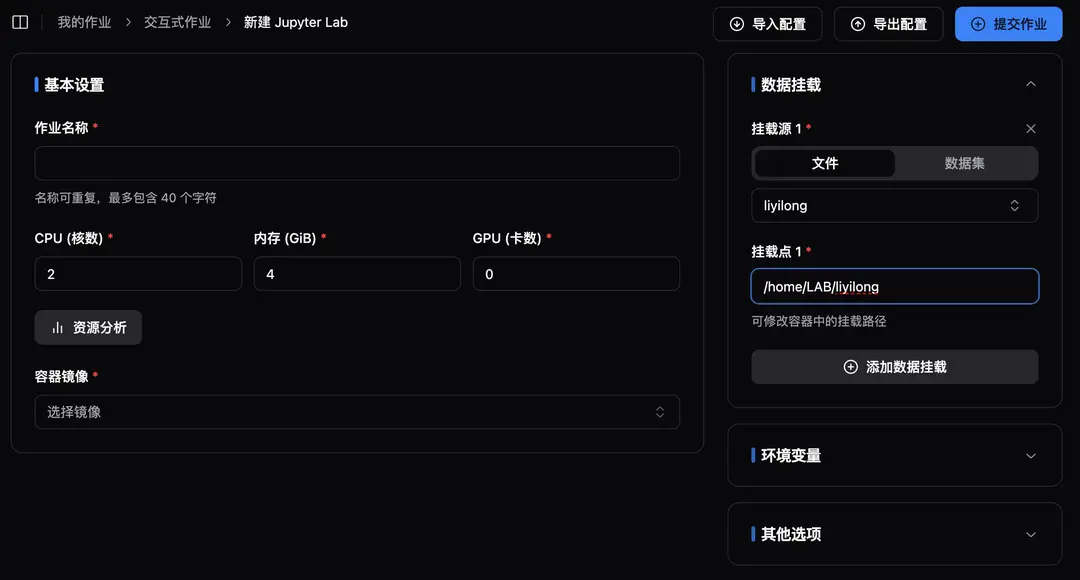
-
Environment activation: Run a command similar to the following to activate the existing environment:
export USERNAME=liyilong export PATH=/home/LAB/${USERNAME}/miniconda3/bin:${PATH} source /home/LAB/${USERNAME}/miniconda3/etc/profile.d/conda.sh export PATH=$CONDA_DIR/bin:${PATH} -
Verify the environment: Use the following command to verify whether the environment is activated successfully:
conda activate
2. Rebuilding a Python Environment Based on an Existing One
Advantages
- Clean environment: Unused dependencies can be removed
- Performance optimization: A new installation typically offers better performance
- Maintainability: A clear list of dependencies facilitates subsequent maintenance
-
Generate Requirements file: Use pipreqs or similar tools to scan the project directory and generate an accurate list of dependencies:
pip install pipreqs pipreqs /path/to/project --encoding=utf8 --force -
Optimize the dependency list:
- Manually check the generated requirements.txt file
- Remove unused dependencies
- Fix version numbers for key dependencies
-
Create a new environment: Please refer to the image creation section for various ways to create a new environment.
Conclusion
We recommend prioritizing the second approach (rebuilding the environment), as it requires more initial work but offers better long-term maintainability and performance. If time is limited, the first approach (reusing the environment) can be used as a temporary solution, but we recommend rebuilding the environment later.
Edit on GitHubNote: When migrating environments, please ensure that you make backups and record all operation steps, so that you can quickly roll back if issues occur.